To provide you with a better browsing experience, this website uses cookies to record and analyze user behavior. The collected data is used solely for statistical and improvement purposes and will not be used to identify you personally.
You can disable cookies in your browser settings, but some features of the website may not function properly.
By continuing to browse this site, you agree to our use of cookies and privacy policy. 👉 View Full Privacy Policy。
service items
/Pregnancy Examinations/
Examination
Basic examination
/Anti-mullerian Hormone/
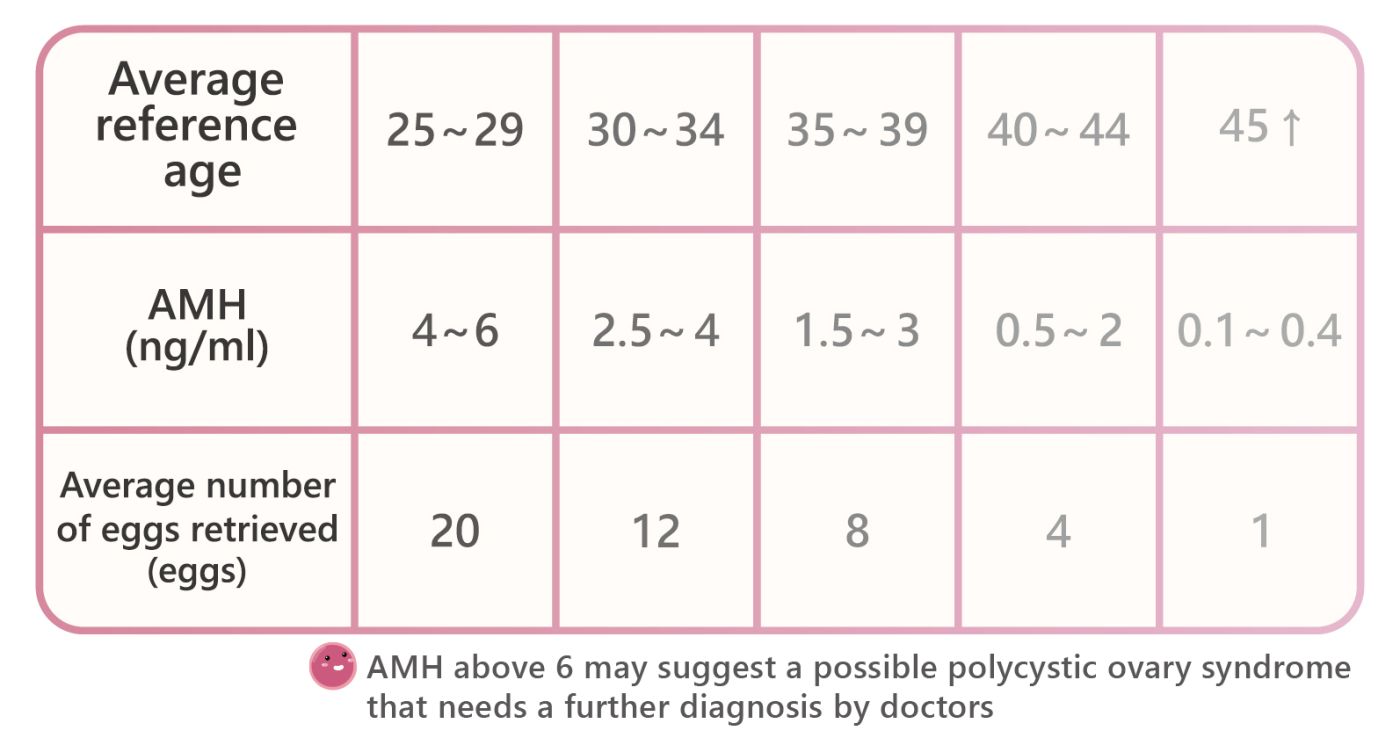
AMH
AMH(Anti-mullerian Hormone),Secreted by the immature small follicles in the ovary, it is an indication of the quantity of follicle reserve in the ovary.
AMH is an index that may be used to evaluate the implementation of artificial fertilization or artificial insemination. It factors heavily in the success of the process.
/inspection/
Examination method
AMH may be obtained by a blood test, and it is not necessary to conduct the test during menstruation. It is recommended that women who plan for pregnancy and unmarried adult women visit a clinic every year to take AMH tests and track the ovarian reserve.
/blood test/
Blood test
-
01. Estradiol
(Estradiol,E2)
Also known as estrogen, it is a steroid hormone secreted by the ovaries. Estrogen is an essential hormone that influences normal female development. It plays multiple critical roles in the female reproductive system, such as regulating the maturation of ovarian follicles and promoting egg development.
A mature follicle can secrete approximately 150 to 300 pg/ml of estrogen, so a higher estrogen level indicates a greater number of mature follicles. -
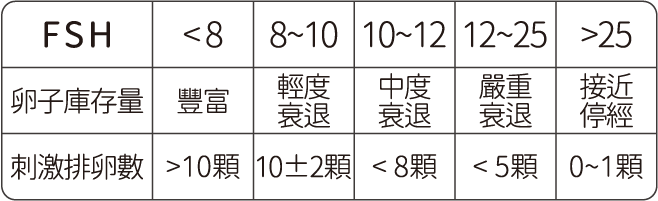
02. Follicle-Stimulating Hormone
(FSH)
FSH is a biological hormone secreted by the anterior pituitary gland that stimulates follicle growth and development. Blood tests during the menstrual cycle can measure FSH levels as an indicator of ovarian reserve. An FSH level above 10 suggests declining ovarian function.
-
03. Luteinizing Hormone
(LH)
LH is a hormone synthesized by the anterior pituitary gland. It plays a key role in follicle development and triggers ovulation by stimulating the release of the egg from the follicle. LH also promotes the production of progesterone and estrogen, as well as the growth of the corpus luteum.
-
04. TSH
(Reference Range: 0.27~4.20 (uIU/ml))
Thyroid-Stimulating Hormone (TSH) is a peptide hormone secreted by thyrotropic cells in the anterior pituitary gland. It regulates the endocrine function of the thyroid gland.
Hypothyroidism may result in elevated TSH levels, leading to menstrual irregularities, ovulation dysfunction, infertility, miscarriage, preterm birth, and an increased risk of preeclampsia. -
05. Prolactin
(Reference Range:25(ng/ml)以下)
Prolactin is primarily responsible for promoting the development and growth of mammary glands and stimulating as well as maintaining lactation. It is secreted by the pituitary gland. However, it interacts with ovarian ovulation hormones, and excessively high levels can inhibit ovulation, leading to infertility.
-
06. Vitamin D
(Calcidiol)
Pregnant women or those planning to conceive are advised to regularly monitor their blood calcidiol levels. If the level is below 30 ng/mL, daily supplementation with Vitamin D3 is recommended to improve egg quality, enhance conception rates, and prevent potential health issues for both the mother and the baby.

/transvaginal ultrasonography/
Transvaginal Ultrasound
Ultrasound helps assess the initial condition of the uterus and ovaries and can predict ovulation around day 11 of the menstrual cycle. At different times, depending on the doctor’s judgment, it can achieve specific diagnostic purposes.
The procedure is similar to a standard gynecological pelvic exam. A thin probe is inserted into the vagina to scan the cervix, uterus, and ovaries using sound waves, which are then converted into images. Compared to abdominal ultrasound, transvaginal ultrasound provides clearer and more accurate results.
Although the invasive nature of the procedure may cause concerns for future mothers, there is no need to worry. A new, dedicated protective sheath is used for the probe during every examination to eliminate the risk of infection, and sound waves are completely harmless to the body.
If you experience any discomfort during the process, notify your doctor immediately.
The procedure is similar to a standard gynecological pelvic exam. A thin probe is inserted into the vagina to scan the cervix, uterus, and ovaries using sound waves, which are then converted into images. Compared to abdominal ultrasound, transvaginal ultrasound provides clearer and more accurate results.
Although the invasive nature of the procedure may cause concerns for future mothers, there is no need to worry. A new, dedicated protective sheath is used for the probe during every examination to eliminate the risk of infection, and sound waves are completely harmless to the body.
If you experience any discomfort during the process, notify your doctor immediately.